Muscle tissue growth and repair are essential for maintaining a healthy body and optimizing physical performance. Recently, the NNMT inhibitor has gained attention in muscle research for its potential impact on these processes. The NNMT inhibitor affects muscle tissue growth and repair, and this can be seen in the 5 amino 1MQ results in recent studies.
Introduction to the 5-amino-1MQ
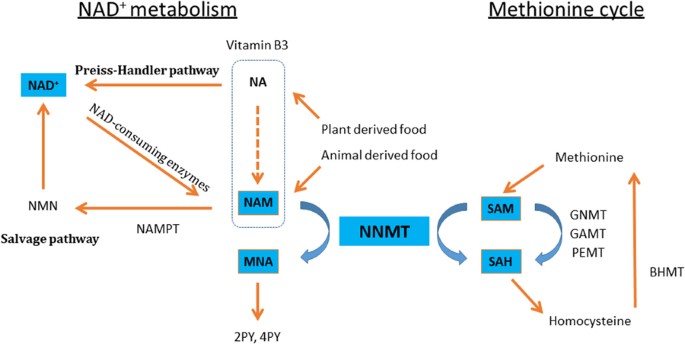
5-amino-1MQ is a compound that has attracted attention in health and wellness. It is an inhibitor of the enzyme NNMT (Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase), which plays a role in regulating metabolism and inflammation in the body. NNMT is involved in methylating nicotinamide (a form of vitamin B3), and its dysregulation has been associated with various health conditions.
By inhibiting NNMT, 5-amino-1MQ has the potential to modulate metabolic pathways and reduce inflammation. This compound has been studied in conditions like obesity, diabetes, and aging-related diseases. It is believed that by interfering with NNMT activity, 5 amino 1MQ may help improve metabolic health, insulin sensitivity, and cellular function.
What is NNMT Inhibitor
The NNMT inhibitor is a compound that targets the enzyme nicotinamide N-methyltransferase. It is responsible for regulating the methyl metabolism pathway, which plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, including muscle tissue growth and repair.
The Role of NNMT in Muscle Tissue
NNMT has been shown to modulate key factors involved in muscle tissue growth and repair. Researchers aim to enhance muscle regeneration and counteract muscle wasting by inhibiting it.
Muscle Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is a fundamental process for muscle tissue growth. NNMT inhibition has been found to promote anabolic signaling pathways, leading to increased muscle protein synthesis. This effect is particularly significant during recovery from exercise-induced muscle damage.
Myogenesis
Myogenesis is the formation of new muscle fibers from precursor cells called myoblasts. Studies suggest that NNMT inhibition can enhance myoblast differentiation and fusion, facilitating muscle regeneration and repair. This could have potential applications in treating muscle injuries and age-related muscle decline.
Muscle Inflammation
Inflammation is a natural response to muscle damage, but excessive or prolonged inflammation can hinder proper tissue repair. The NNMT inhibitor has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties by reducing the production of pro-inflammatory molecules. This anti-inflammatory effect may promote a more efficient healing process.
Research Findings and Potential Applications
Several studies have investigated the impact of NNMT inhibition on muscle tissue growth and repair, yielding promising results. These findings have sparked interest in potential applications of NNMT inhibitors in various scenarios, including:
Muscle Injury Recovery
By promoting muscle protein synthesis and reducing inflammation, NNMT inhibitors may accelerate recovery after muscle injuries. This could be beneficial for athletes or individuals undergoing rehabilitation.
Age-Related Muscle Decline
Age-related muscle loss, or sarcopenia, is common among older adults. NNMT inhibitors could potentially counteract muscle wasting and improve muscle function in aging populations.
Muscle Disorders
Certain muscle disorders, such as muscular dystrophy, involve impaired muscle regeneration and progressive muscle weakness. NNMT inhibition might offer a therapeutic approach to enhance muscle repair and slow down disease progression.
Conclusion
With NNMT inhibitors like 5 amino 1mq, the results show promising potential for enhancing muscle tissue growth and repair. These effects suggest a potential avenue for optimizing muscle recovery, combating age-related muscle decline, and even addressing debilitating muscle disorders.
As the scientific community delves deeper into the mechanisms and applications of NNMT inhibitors, the potential benefits they hold for muscle tissue growth and repair become increasingly evident. It is an exciting time of discovery and innovation, offering hope for improved athletic performance, enhanced quality of life in older adults, and potential breakthroughs in treating muscle-related disorders.